
Many infections cause no symptoms in healthy people. The immune system, inhibits the activity of the Virus, which the human being is a carrier of the infection. The transmission of the pathogen to other people occurs even in the case of full clinical well-being, because the virus particles in the body fluids of the patient. Latent infections can be a major reason of great spread of the disease: the patient happen in a timely investigation, and will continue to infect other people irresponsible.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) can also be referred to as an excellent example of a latent infectious agent. Most people do not get infected, at least one type of HPV during their lifetime, however, the clinical symptoms of the disease occur far not in all cases. To bring the distant complications of the infection, the doctors are at increased risk for the formation of a malignant tumor. In patients with immune deficiency, often a negative consequence of the disease occurs. Topical medications will help symptoms to suppress HPV infection. Also, we recommend the timely vaccination.
More about the disease
Human Papilloma Virus, the causative agent of the infections, homeopath is on the skin and the mucous membranes of the organs. The main Manifestation of the disease is the growth of tumors in the area of the face, the genitals, the oral cavity and the pharynx. In some cases, Spitzer papillomas develop in non-specific areas, such as the skin of the lower and upper extremities. The localization of the warts depends on the type of HPV. For most people, the infection leads to a hidden carriage of infection, however, due to the reduction of immunity, the Virus begins its toxicity. In some cases, immune competent cells to destroy themselves pathogens within 3-6 months after its Invasion in the body.
HPV infection is the most common sexually transmitted disease. This figure explains the high virulence of the Virus and the asymptomatic course of the pathology in the majority of a people can be. The use of condoms is not always possible to avoid infection, so that the Patient can spread even further, the Virus even when protected intercourse. At the same time, experts developed effective vaccines, the development of oncogenic forms of HPV. The immunization shows a teenage girls, because of the protection against the Virus is to convey, before the first sexual contact.
The properties of the Virus
Human Papilloma Virus is DNA-containing pathogens, ends. In contrast to bacteria and other microorganisms, viruses are able to show their activity after introduction into the cell and the embedding of the own genetic Information in the nucleus. Thereafter, the affected cell begins to synthesize proteins required for the Assembly of virus particles. Almost all members of the family man attack, only one type of organisms, where HPV infection can only occur in humans.
Scientists know more than 600 strains (types) of human Papillomavirus, the different genetic information. 40 types of HPV can cause different forms of lesions of the mucous membranes and the skin. Important clinical significance are strains of the classification of the degree of oncogenetic. So, cervical cancer in women most often occurs in infection with HPV types 16 and 18. These infectious agents do not always occur changes in the skin.
HPV infects the basal layer of the epithelial cells. The pathogens can be in the Form of episome, are not associated with the cellular DNA, or an integrated Form in connection with the genome of the cell. Just built-in Virus produces the necessary proteins and causing the clinical symptoms of the disease. Foundations of life HPV in the body is not the immediate cause of the malignant Transformation of tissues, however, carriers of the Virus increases the risk of risk factors for cancer.
Methods of infection
The Virus contains the basal cells of the epithelium, so that all the micro-traumas of the skin and of the mucous membranes increase the risk of infection. In the cases most a HPV is through vaginal, anal, or oral sexual contact. A condom only part of the surface of the skin can be protected, however, the virus particles are penetrating yet can cover in the body by others. The presence of genital warts predisposes to the transmission of the pathogen, but outwardly intact skin, the carrier of the disease is also a source of HPV.
Other routes of transmission
- Infection of the child during birth. Most common in children lesions of the respiratory tract occur
- The independent transmission of the Virus from one body part to another
- General use of objects of personal Hygiene, including razors, toothbrushes and towels
- The Transfusion of blood. Recent studies have confirmed the possibility of transfusion infection.
- Surgical procedures in non-sterile conditions
Despite the diverse causes of viral infection, only the sexual way of infection with HPV has clinical significance. Other sources of infection due to the low risk of the spread of the pathogen.
Risk factors
In addition to the direct transmission of HPV, have also the role of the risk factors are taken into account. It's about the way of life of the people, and certain physical conditions.
The most important risk factors for infections
- A large number of sexual partners. Even with Safer Sex an active sex life sooner or later leads to infection.
- Age. Genital warts are identified in the majority of cases, in adolescents and younger patients, while the warts of the oral cavity and the respiratory tract is characteristic for children.
- A weakened immune system. Patients suffering from HIV-infection or acquired immunodeficiency, are at a higher risk of viral infection. Also, HPV often manifests itself symptomatically after organ transplantation.
- Damage to the skin and mucous membranes. Microtrauma to facilitate the penetration of the Virus into the basal layer of the epithelium.
- Smoking and alcoholism. Bad habits weakened activity of the immunity.
- Urogenital Infection.
In addition, in the group of risk of infection, pregnant women are. Note that the elimination of the factors of predisposition to the disease an effective preventative tactics.
jpg" class="imgblock right center_mob">The clinical course
The incubation period before symptomatic manifestation of the disease, it can take several months or not. In immunocompetent patients during this time, the body can destroy the infection, but spontaneous elimination of the pathogen does not always happen. A Person can at the same time with multiple strains of the Virus. Signs of HPV infection arise at influence of unfavorable factors, the weakening of the immune defense of the tissue. Due to return currents acuminata disappear at regular intervals and re-formed. Oncological complications of infection can. in the course of several decades
Possible consequences of the disease:
- Carcinoma of the cervix – malignant epithelial tissue. This type of cancer only with the human Papilloma Virus. With timely vaccination, the risk of oncogenesis is reduced.
- Squamous cell cancer of the Anus. This complication can occur in both men and women. Early symptoms of cancer of the anus include bleeding and itching.
- Violation of urination due to obstruction of the urethra the warts.
- Malignant transformation of warts in the area of the pharynx and the oral cavity.
Cervical cancer is one of the most common causes of death of women. As this disease is passage needs associated with viral Invasion of regular check-UPS at the gynecologist. Modern vaccines protect women against the oncogenic HPV types.
Diagnosis
Investigation, the warts gynecologist, urologist, venereal diseases, and dermatologists deal. During primary intake, the doctor questioned the patient about the complaints and anamnestic data, and the inspection of the formations. In General, HPV symptoms are easy to identify, but need to exclude other diseases. To do this, the specialist will prescribe Instrumental and laboratory investigations.
The necessary methods of diagnostics:
- Instrumental examination of the vagina and cervix (colposcopy). Such investigations are necessarily carried out Screening for cervical cancer. During the examination the doctor can detect, multiple papillomas, and areas of epithelial dysplasia.
- Biopsy – receiving fabric material in the area of the skin or mucous membrane changes. Cytological examination of the specimen allows for the identification of malignant cells.
- Polymerase chain reaction detection of virus particles HPV in the body. The implementation of this Test gives the doctor the ability to determine the root of the disease pathogen and viral load.
- Digene-Test – high-precision identification of DNA-oncogenic strains of human Papillomavirus. The research used as a reliable Screening.
Drug Treatment
Developed drugs against HPV infection can only eliminate the symptoms of the disease and to prevent malignancy tissue. The complete elimination of the Virus by drug therapy is not possible. Examine oral and topical agents will be assigned in the case of a high risk of oncogenesis, immune weakness, and other adverse conditions. If the Virus shows itself from external changes, be enough for General prevention measures.
Possible Assignments
- Salicylic acid for the removal of warts. Not to be used for the treatment of the skin of the face and genitals.
- Creams and ointments, the immunomodulating agent.
- Podofilox ointment with cytotoxic effect. The application of medication to the affected skin leads to the destruction of the pathogenic elements.
- Trihloruksusnaya acid for chemical burns in General, and genital warts. Cause local expression of chap.
These drugs should only under medical supervision. After the removal of warts, HPV infection can occur, and even spread to other areas.
Surgical Treatment
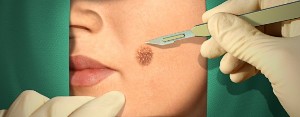
The doctor may to the patient, the surgical and minimally invasive procedures to remove warts. In General, such methods will not cause any complications, but in the first days after the surgery, bleeding tissue can occur.
Types of interventions:
- conventional surgical excision;
- freezing with liquid nitrogen and subsequent destruction of diseased tissue;
- electric coagulation;
- the papillomas delete with a Laser.;
- the use of radio wave "knife".
All procedures are performed under local anesthesia. Specialist selects the first method for the treatment of warts.
Prediction
While HPV infection depends on the immune status of the patient and the specific strain of the virus. About 30% of the population, there is a spontaneous Elimination of the pathogen of the disease, due to the active immunity. Symptomatic for the disease often manifests in pregnant women, children, the elderly and patients with immune deficiency.
For HPV-infection is characterized by relapsing course. The papillomas can gradually fade or spread on the adjacent skin. Oncogenic strains of the Virus most often the mucous membrane of the cervix, appearance, infect, wherein epithelial dysplasia reinforces the effect of the risk factors of malignant Transformation of tissues, such as Smoking and the use of oral contraceptives. The Tumor can be formed, in 10-20 years after infection of the Virus in the organism.
Prevention
The most reliable method of prevention is early immunization. The vaccine "Gardasil", the viral proteins and in addition to aggregates, to be effective against HPV 6, 11, 16 and 18 types. If the vaccination is carried out at an early age before the first sexual contact, the risk of the later development of cervical cancer in women, no more than 1%.
Additional Prevention:
- the use of condoms;
- Sex only with reliable partners;
- careful personal Hygiene;
- gynecological examination at least once in a year.

























